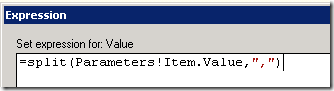
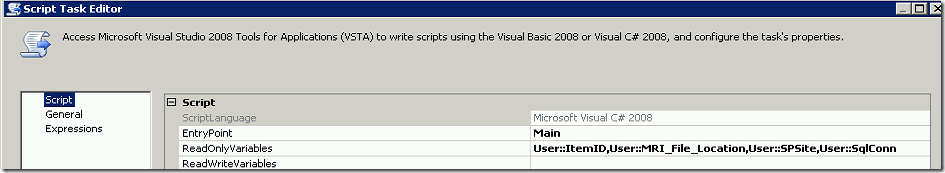
You’ll want to read my previous post Moving SharePoint List Attachments to the File System, to get all the details and requirements for setting up and running these SSIS script tasks.
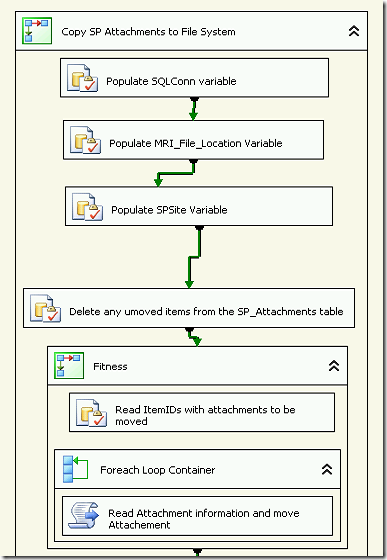
This is an SSIS Package code which will iterate through the document library to get some relevant information about the documents, and then move specified documents from a document library to the file system.
I will just explain the two script tasks steps, as the rest will be specific to your task.
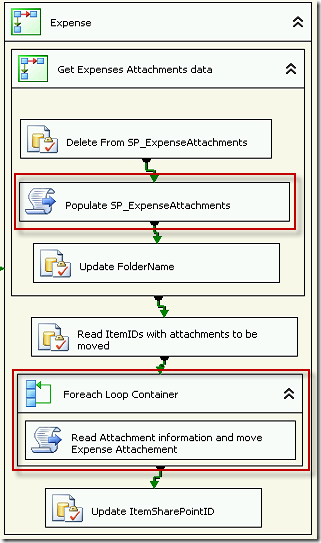
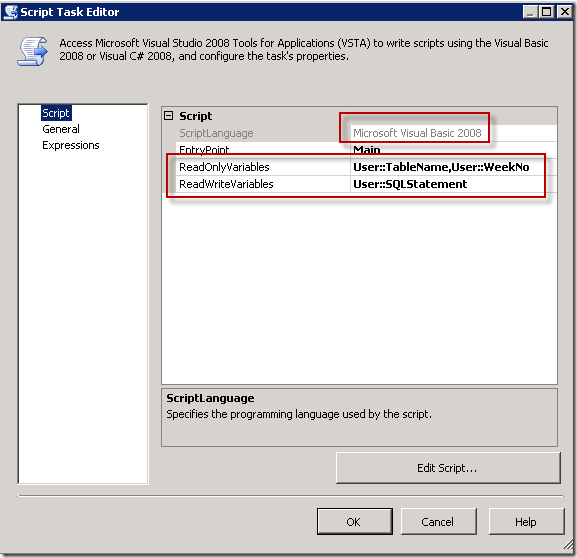
Populate SP_ExpenseAttachments Sript Task
This code iterate through the document library to get some relevant information about the documents
using System;
using System.Data;
using Microsoft.SqlServer.Dts.Runtime;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO;
using Microsoft.SharePoint;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Net;
namespace ST_573f63e769424529b4c14ec196d01e4f.csproj
{
[System.AddIn.AddIn("ScriptMain", Version = "1.0", Publisher = "", Description = "")]
public partial class ScriptMain : Microsoft.SqlServer.Dts.Tasks.ScriptTask.VSTARTScriptObjectModelBase
{
#region VSTA generated code
enum ScriptResults
{
Success = Microsoft.SqlServer.Dts.Runtime.DTSExecResult.Success,
Failure = Microsoft.SqlServer.Dts.Runtime.DTSExecResult.Failure
};
#endregion
/*
The execution engine calls this method when the task executes.
To access the object model, use the Dts property. Connections, variables, events,
and logging features are available as members of the Dts property as shown in the following examples.
To reference a variable, call Dts.Variables["MyCaseSensitiveVariableName"].Value;
To post a log entry, call Dts.Log("This is my log text", 999, null);
To fire an event, call Dts.Events.FireInformation(99, "test", "hit the help message", "", 0, true);
To use the connections collection use something like the following:
ConnectionManager cm = Dts.Connections.Add("OLEDB");
cm.ConnectionString = "Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=AdventureWorks;Provider=SQLNCLI10;Integrated Security=SSPI;Auto Translate=False;";
Before returning from this method, set the value of Dts.TaskResult to indicate success or failure.
To open Help, press F1.
*/
public void Main()
{
// Read the Library document info and write it to a SQL table
string SharePointSite = (string)Dts.Variables["SPSite"].Value;
SPSite mySite = new SPSite(SharePointSite);
SPWeb myWeb = mySite.OpenWeb();
SPList myList = myWeb.Lists["ExpenseAttachments"];
SPDocumentLibrary myLibrary = (SPDocumentLibrary)myList;
SPListItemCollection collListItems = myLibrary.Items;
foreach (SPListItem myListItem in collListItems)
{
String ItemId = myListItem.ID.ToString();
String attachmentAbsoluteURL = SharePointSite + "/" + myListItem.File.Url;
String attachmentname = myListItem.File.Name;
//Set up SQL Connection
string sSqlConn = Dts.Variables["SqlConn"].Value.ToString();
SqlConnection sqlConnection1 = new SqlConnection(sSqlConn);
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand();
SqlDataReader reader;
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.Text;
cmd.Connection = sqlConnection1;
sqlConnection1.Open();
cmd.CommandText = "INSERT INTO SP_ExpenseAttachments (WorkflowName,DocumentLibrarySharePointID,AttachmentName,AttachmentURL) VALUES ('Expense','" + ItemId + "','" + attachmentname + "','" + attachmentAbsoluteURL + "')";
reader = cmd.ExecuteReader();
sqlConnection1.Close();
}
Dts.TaskResult = (int)ScriptResults.Success;
}
}
}
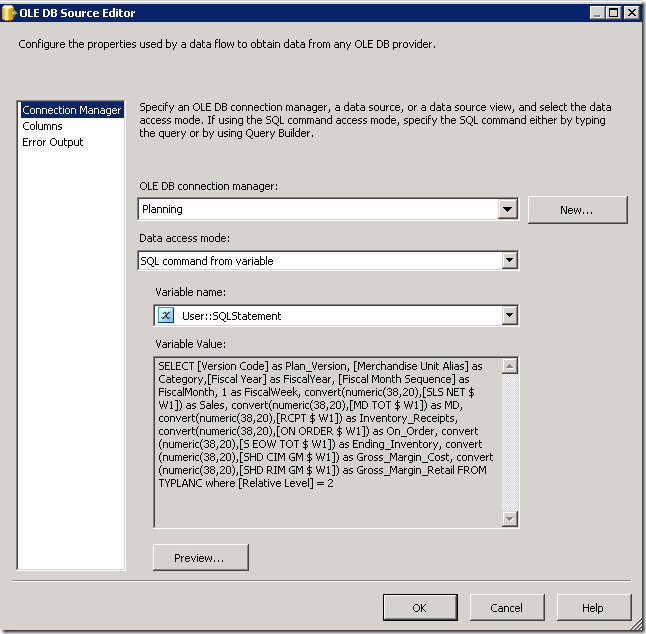
Read Attachment information and move Expense attachments
This code accepts a document id from a variable, populates some relevant information about the document into a SQL table and copies and renames the document to the file system.
using System;
using System.Data;
using Microsoft.SqlServer.Dts.Runtime;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO;
using Microsoft.SharePoint;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Net;
namespace ST_573f63e769424529b4c14ec196d01e4f.csproj
{
[System.AddIn.AddIn("ScriptMain", Version = "1.0", Publisher = "", Description = "")]
public partial class ScriptMain : Microsoft.SqlServer.Dts.Tasks.ScriptTask.VSTARTScriptObjectModelBase
{
#region VSTA generated code
enum ScriptResults
{
Success = Microsoft.SqlServer.Dts.Runtime.DTSExecResult.Success,
Failure = Microsoft.SqlServer.Dts.Runtime.DTSExecResult.Failure
};
#endregion
/*
The execution engine calls this method when the task executes.
To access the object model, use the Dts property. Connections, variables, events,
and logging features are available as members of the Dts property as shown in the following examples.
To reference a variable, call Dts.Variables["MyCaseSensitiveVariableName"].Value;
To post a log entry, call Dts.Log("This is my log text", 999, null);
To fire an event, call Dts.Events.FireInformation(99, "test", "hit the help message", "", 0, true);
To use the connections collection use something like the following:
ConnectionManager cm = Dts.Connections.Add("OLEDB");
cm.ConnectionString = "Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=AdventureWorks;Provider=SQLNCLI10;Integrated Security=SSPI;Auto Translate=False;";
Before returning from this method, set the value of Dts.TaskResult to indicate success or failure.
To open Help, press F1.
*/
public void Main()
{
// Read the document info and write it to a SQL table
string SharePointSite = (string)Dts.Variables["SPSite"].Value;
SPSite mySite = new SPSite(SharePointSite);
SPWeb myWeb = mySite.OpenWeb();
SPList myList = myWeb.Lists["ExpenseAttachments"];
SPDocumentLibrary myLibrary = (SPDocumentLibrary)myList;
SPListItemCollection collListItems = myLibrary.Items;
int ItemID = (int)Dts.Variables["ItemID"].Value;
String sItemID = ItemID.ToString();
SPListItem myListItem = myList.GetItemById(ItemID);
String attachmentAbsoluteURL = SharePointSite + "/" + myListItem.File.Url;
String attachmentname = myListItem.File.Name;
//Set up SQL Connection
string sSqlConn = Dts.Variables["SqlConn"].Value.ToString();
SqlConnection sqlConnection1 = new SqlConnection(sSqlConn);
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand();
SqlDataReader reader;
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.Text;
cmd.Connection = sqlConnection1;
sqlConnection1.Open();
cmd.CommandText = "INSERT INTO SP_Attachments (WorkflowName, DocumentLibrarySharePointID, AttachmentName, AttachmentURL, Moved, NewFileName) VALUES ('Expense','" + ItemID +"','" + attachmentname + "','" + attachmentAbsoluteURL + "','" + 0 + "','E' + RIGHT('00000000000' + CAST(" + ItemID + " as VARCHAR),11)" + ")";
reader = cmd.ExecuteReader();
sqlConnection1.Close();
string MRI = (string)Dts.Variables["MRI_File_Location"].Value;
DirectoryInfo dir = new DirectoryInfo(MRI);
if (dir.Exists)
{
// Create the filename for local storage using
String FileExt = attachmentname.Substring(attachmentname.Length-4);
String ItemNum = "00000000000" + sItemID;
String ItemName = ItemNum.Substring(sItemID.Length, 11);
String FileName = "\E" + ItemName + FileExt;
FileInfo file = new FileInfo(dir.FullName + FileName);
if (!file.Exists)
{
if (attachmentAbsoluteURL.Length != 0)
{
// download the file from SharePoint or Archive file system to local folder
WebClient client = new WebClient();
//download the file from SharePoint
client.Credentials = System.Net.CredentialCache.DefaultCredentials;
client.DownloadFile(attachmentAbsoluteURL, file.FullName);
}
//Mark record as Moved
sqlConnection1.Open();
DateTime Now = DateTime.Now;
cmd.CommandText = "UPDATE SP_Attachments SET Moved = 1, Moved_Date = '" + Now + "' WHERE WorkflowName = 'Expense' and DocumentLibrarySharePointID = '" + ItemID + "'";
reader = cmd.ExecuteReader();
sqlConnection1.Close();
}
Dts.TaskResult = (int)ScriptResults.Success;
}
}
}
}