I have a situation where there is an alternate authentication method in place on SharePoint and deploying reports using the Visual Studio deployment options won’t work. To get around this while they sort it out I have manually loaded the reports, data sources and shared datasets to SharePoint. There were a few tricks which I would like to remember so I’ll post them here.
1. Create 3 document libraries:
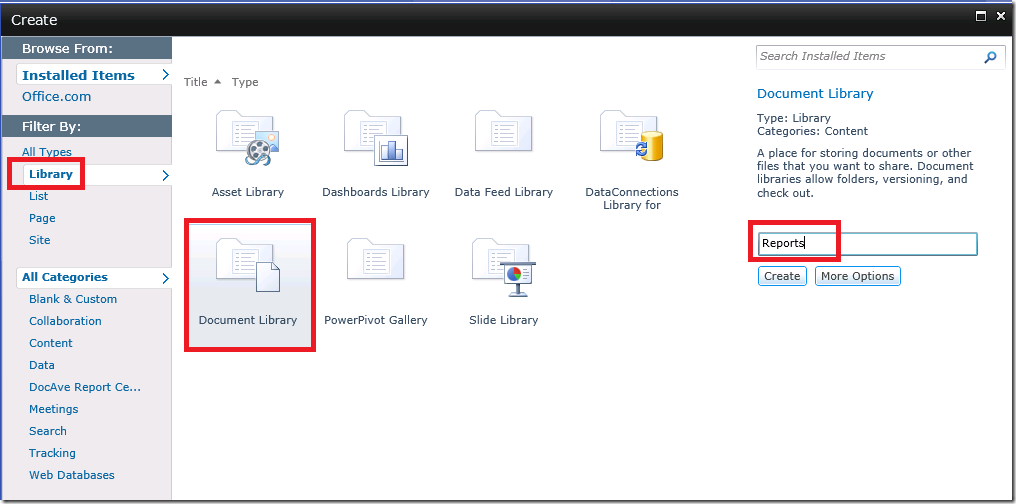
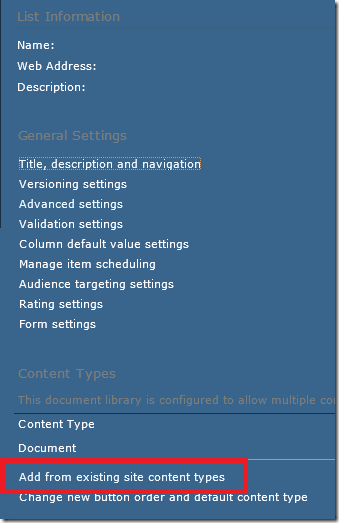
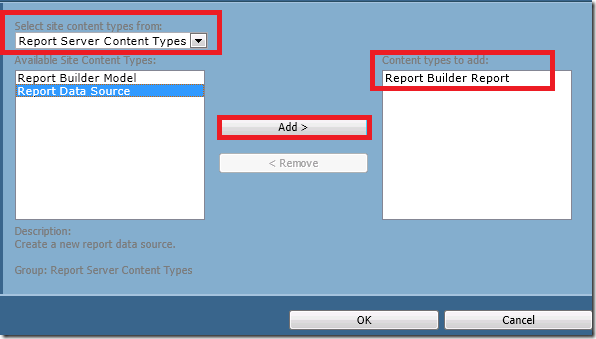
The first thing I did was create three libraries, one for Reports, one for Shared Datasets and one for Shared Data Sources. You don’t have to have separate libraries, but I find it more user friendly to keep these items separate. I don’t want users weeding through data sets and data sources to get to their reports. Here is how to create these libraries. The one surprise is to use a content type of Report Builder Report for the Shared Datasets. I imagine this is to allow you to configure your Dataset to connect to a Data Source.
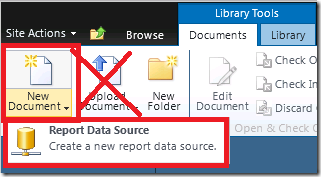
2. Create (don’t upload) the Data Source.
Navigate to the Data Source library you created. From the Documents tab select New Document. Do not try to upload a data source you have already created for your report, since, for whatever reason, SharePoint won’t recognize it as a Report Data Source. You need to recreate it.
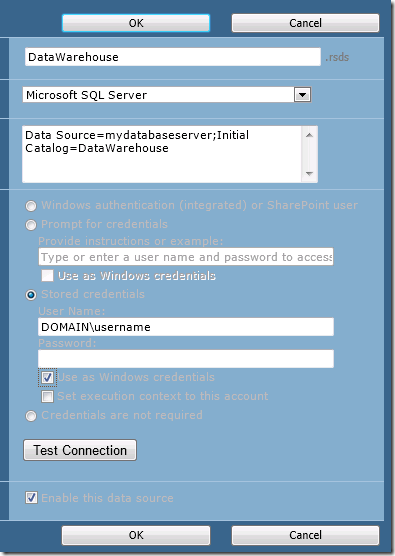
Configure the data source appropriately. Choose “Stored Credentials” to allow for proxy authentication, and select “Use as Windows credentials”. Click on the Test Connection button to be sure it is working. Click OK.
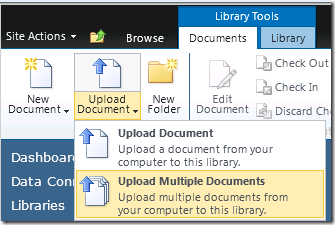
3. Upload the Shared Datasets:
Navigate to your Shared Datasets library and from the Documents tab you can “Upload Document” or “Upload Multiple Documents” depending on how many shared datasets you have.
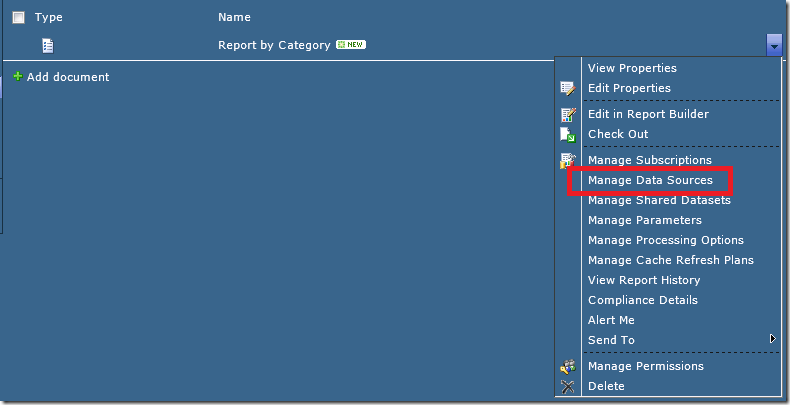
4. Connect the Shared Datasets to the Data Source:
Connect the shared datasets to the appropriate data source. Click the drop down beside the dataset and select “Manage Data Sources”.
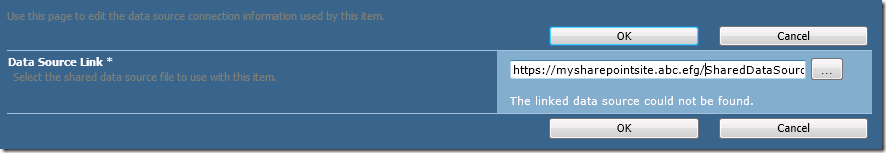
Click on the “DataSetDataSource”, which will have the yellow caution triangle to let you know it has not been configured.
Click on the ellipsis and navigate to wherever you created the data source in SharePoint.
Click OK and click Close. Do this for all the Shared Datasets you uploaded.
5. Upload the Report:
Navigate to the Report library you created. From the Documents tab select Upload Document and upload your Report Services report.
6. Connect the Report to the Data Source:
From the drop down beside the report select “Manage Data Sources”.
Same as step 4, click on the name of the data source that needs to be connected. Click on the ellipsis and navigate to where the data source is stored in SharePoint. Click OK. Click Close.
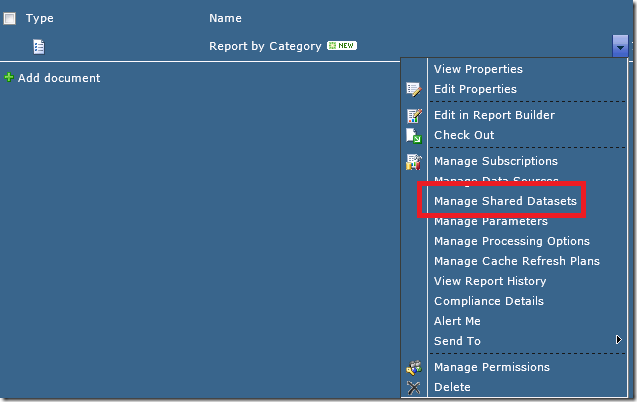
7. Connect the Report to the Shared Datasets:
From the drop down beside the report select “Manage Shared Datasets”
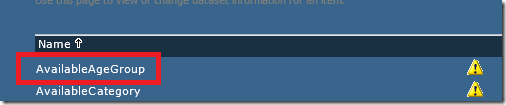
From the list of dataset names which need to connected, click on the first one which has a yellow caution triangle beside it. This lets you know that the dataset has not yet been connected.
Click on the ellipsis and navigate to where you have stored your shared datasets. Select the dataset. Click OK. Repeat this for any shared datasets which have not been connected. Click Close.
You are ready to view your report. If you get any data source errors, check that the Shared Datasets are all connected correctly to the data source, as well as the report.